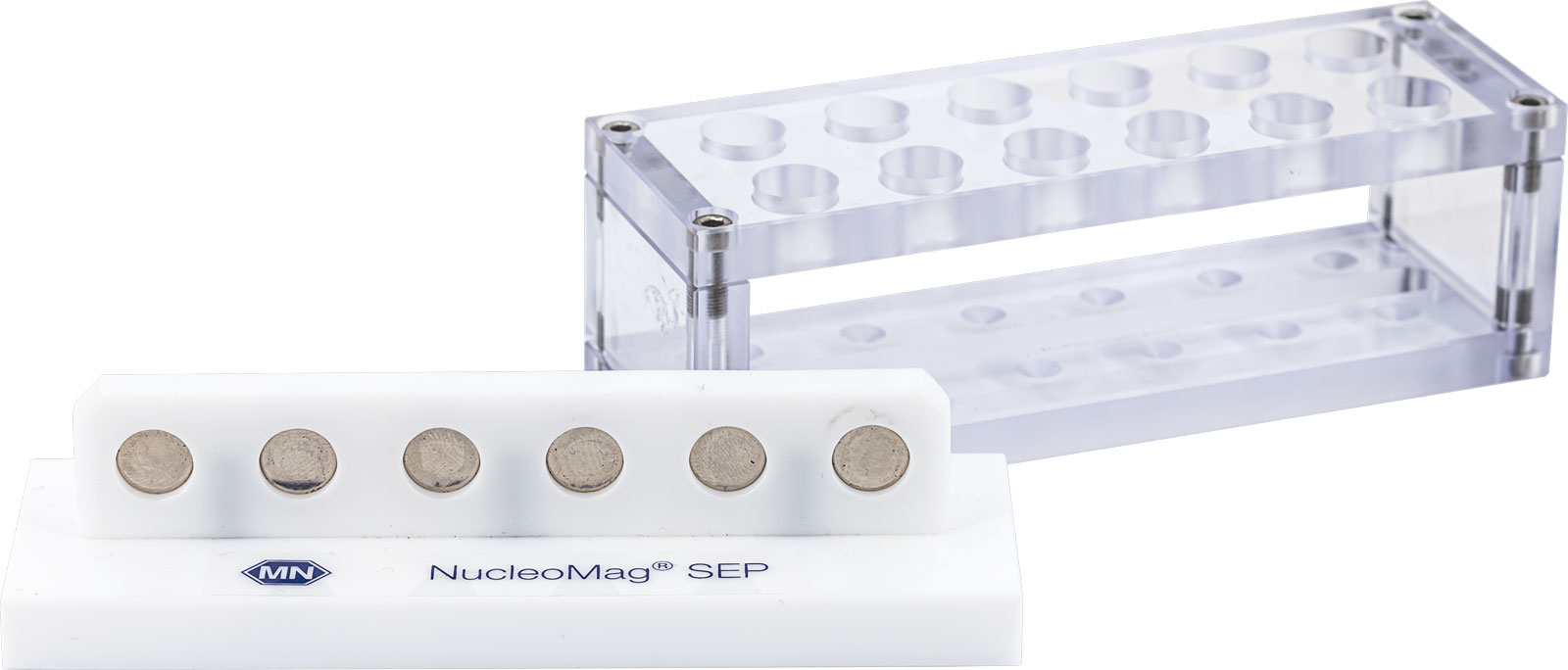
NucleoMag SEP Mini
*taxes and shipping not included
Delivery time approx. 5 working days
Magnetic separator, for use with 12 x 1.5 mL or 2 mL reaction tubes
| Application | Other |
| Brand | NucleoMag |
| Target | Accessories |
| Format | Magnetic beads |
| CE certified | No, research use only |
| Handling | Magnetic separation |
| Scope of delivery | Magnetic separator |
| Storage temperature | 15–25 °C / 59–77 °F |
| Gross weight (incl. packaging) | 364.25 g / 0.8 lbs |
| Packaging dimensions | 151 x 110 x 83 mm / 5.94 x 4.33 x 3.27 Inch |
| Hazardous material | No |
Manual processing of magnetic beads with NucleoMag SEP Mini
1) Addition of NucleoMag beads to the cleared lysate

2) Resuspend beads completely - rack can directly be placed on a vortex mixer




3) Magnetic separation - Place resuspended beads on the magnetic stand
5) Magnetic separation - Remove supernatant and continue with next washing step
Standard microcentrifuge tubes (<2mL) can easily be processed with our NucleoMag SEP Mini. The sample rack detaches easily from the base magnet for resuspension, vortexing, rotation, manual sample shaking or even tube storage. Ideal for convenient, parallel handling of multiple samples. The magnet can of course be used with all types of NucleoMag beads for efficient isolation of nucleic acids.
The following video demonstrates how our NucleoMag SEP Mini can be used to conveniently isolate nucleic acids based on magnetic bead technology.
Drying of beads prior to elution
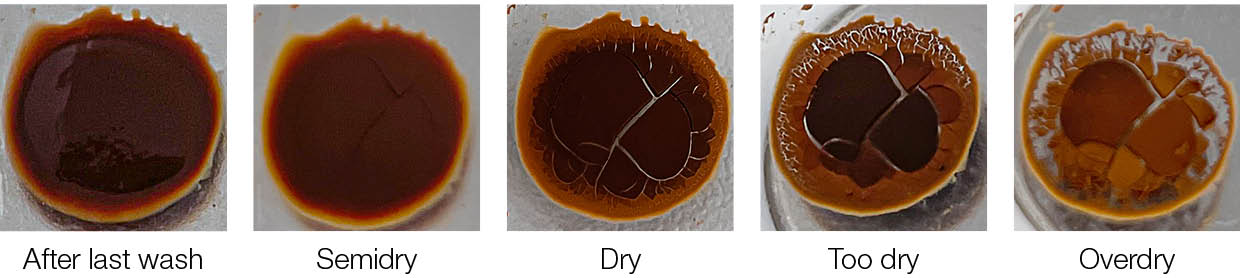

6) Airdry magnetic beads after last washing step - please find our recommendations below
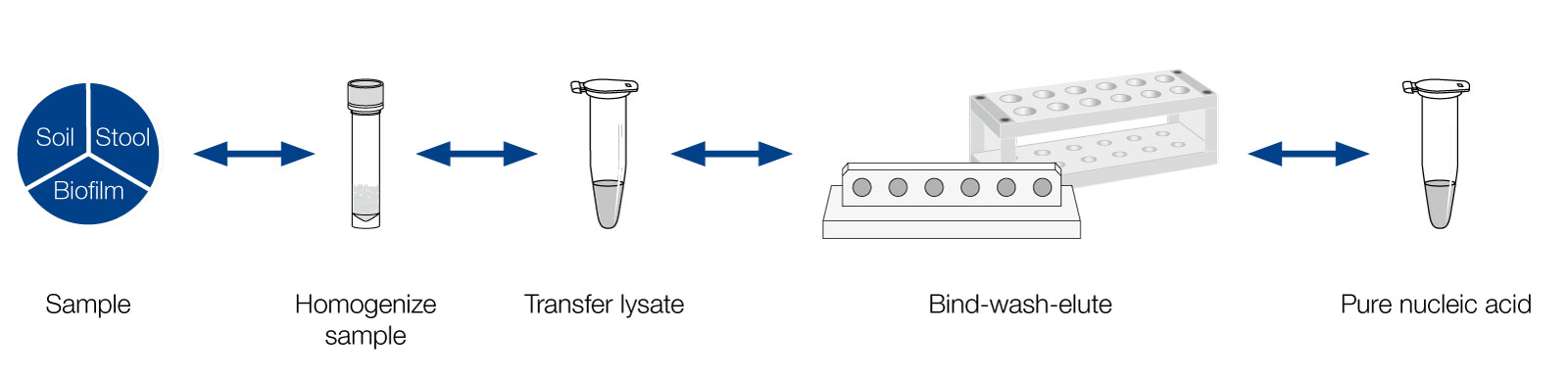
Magnetic beads can be integrated in various isolation workflows. Depending on the combination with suitable buffers, different kind of sample materials can be processed including plant leaves, stool, soil, food matrices, tissue among others. First the sample is lysed. For several sample materials mechanical sample disruption with MN Bead Tubes is recommended. Afterwards, the cleared lysate is transferred to a suitable reaction tube. Then binding buffer and magnetic beads are added to bind nucleic acids to the beads. Several washing steps are performed with the beads attracted to the magnet allowing to discard the supernatant. As a final step the pure nucleic acid is eluted.
4) The beads are attracted to the magnet - follow the recommended time to allow complete attraction
Before elution of nucleic acids, the beads are dried after the last wash step. It is very important to assure all the ethanol has evaporated without overdrying the beads. Overdrying of the beads might cause difficulties in resuspending the nucleic acids in elution buffer resulting in reduced yields. However, if the beads are too wet, bad purities and/or inhibiton may occur. Below you can find a progression pointing out the ideal drying state.
















Purification workflow











