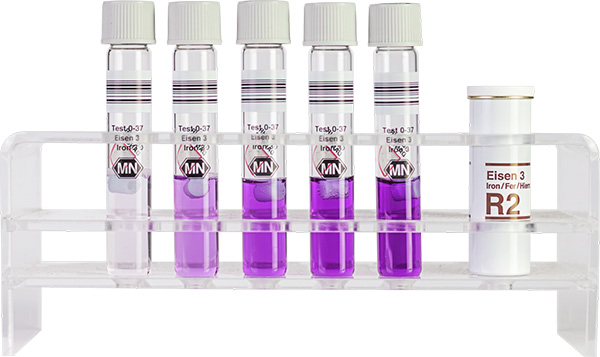
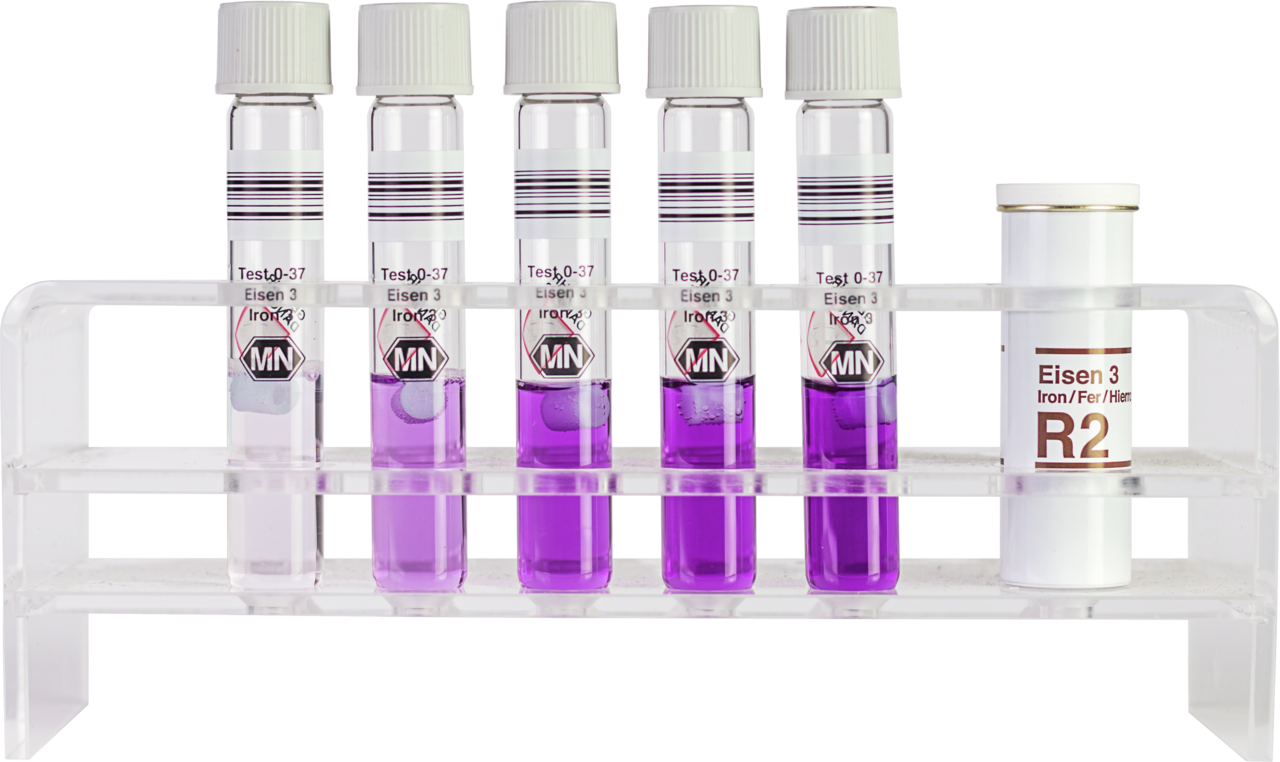
Tube test NANOCOLOR Iron 3
*taxes and shipping not included
Delivery time approx. 5 working days
Tube test for the determination of Iron. Precise rapid tests for all kind of water and waste water samples. Time-saving and reliable analysis together with our NANOCOLOR photometers.
| Brand | NANOCOLOR |
| Platform | NANOCOLOR tube tests |
| Parameter | Iron |
| Measuring range | Iron - 0.10–3.00 mg/L Fe |
| Measuring range sensitive | Iron - 0.02–1.00 mg/L |
| Sludge reagent set | No |
| Test No. | 0-37 |
| Evaluable on | 500 D, Advance, MT Easy UV, MT Easy VIS, PF-12Plus, UV/VIS II, VIS II |
| Method | Iron - Diphenylpyridyltriazine |
| NanOx N | No |
| NanOx Metal | Yes |
| Crack-Set | Yes |
| Sea water analysis | Yes |
| Remark | Measuring range on NANOCOLOR VIS II |
| Shelf life (from production) | 1.5 Year(s) |
| Storage temperature | 15–25 °C / 59–77 °F |
| Scope of delivery | Rugged box with 20 test tubes. Sufficient for 20 tests. |
| Gross weight (incl. packaging) | 344 g / 0.76 lbs |
| Packaging dimensions | 160 x 110 x 119 mm / 6.30 x 4.33 x 4.69 Inch |
| Hazardous material | Yes |
- Download Instruction / Anleitung / Manuel
- Download Pictogram / Piktogramm / Pictogramme
- Download Validation data / Validierungsdaten / Données de validation
- Download Betriebsanweisung (DE)
- Download Flyer NANOCOLOR analysis system (EN)
- Download Flyer Das NANOCOLOR Analysensystem (DE)
- Download Flyer Système d’analyse NANOCOLOR (FR)

Iron
As one of the most abundant elements, iron is ubiquitous in our daily lives. Iron salts are essential for human life and are absorbed through food and drinking water. However, excessive concentrations of iron in water are undesirable due to discoloration and the formation of deposits such as rust.
How to perform the NANOCOLOR Iron 3 tube test
General information
With 6.2 %, iron is the 4th most abundant element in the earth’s crust and, after aluminum, the second most abundant metal. In water, it is present in various forms. Groundwaters with low oxygen levels and reducing medium often have iron contents of above 0.1 mg/L. The divalent iron(II) Fe2+ is particularly sensitive to air. It is oxidized by atmospheric oxygen to form trivalent iron(III) Fe3+, which precipitates as a brown, fuzzy-amorphous iron oxide hydrate due to its low solubility. Furthermore, the presence of iron is also pH-dependent. At pH values above 8, iron(II) ions Fe2+ are converted to poorly soluble iron(II) hydroxides.
Dissolved iron can limit the use of the water for consumers because precipitation can occur upon use of the water, for example in laundering. Iron in drinking water is undesirable because it leads to brown color and foul odor.
At the usually present concentrations, iron (and manganese) poses no direct health risk to humans. However, in drinking water these compounds are undesirable because they can form deposits in the pipe network that increase the flow resistance to a considerable extent. Consequences of this are firstly unwanted discolorations, on the other hand so-called secondary microbial contaminations due to corresponding iron and manganese bacteria.
The main application of iron is in the steel and metal industry. Due to its easy availability, strength and toughness, iron is one of the most important base materials. Iron is also used, amongst other things, as a flocculating agent. Determination of dissolved iron is an important indicator of the extent of corrosion.
Reaction basis
All test kits are based on one of two different reaction principles:
(a) Triazine method:
Iron(II) ions react with a triazine derivative to form an intensely colored purple complex.
Triazine derivatives are highly miscible with thioglycolic acid. Thioglycolic acid is used for the reduction of iron(III) to iron(II), and for pH adjustment. Thus only one reagent is required for analysis.
Test kits VISOCOLOR ECO Iron 1, VISOCOLOR ECO Iron 2, VISOCOLOR HE Iron, NANOCOLOR Iron 3, and NANOCOLOR Iron LR are based on this method.

R = H, SO3H
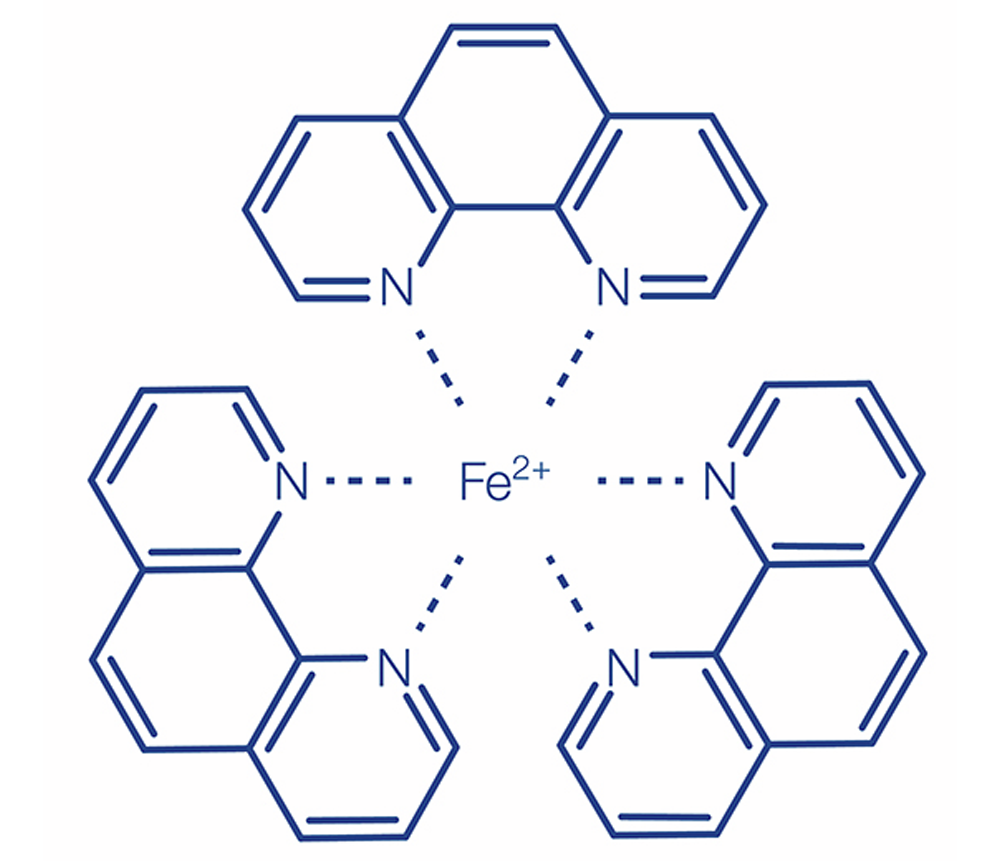
(b) DIN method analogous to APHA 3500-Fe D, DIN 38406-E1-1, ISO 633:
Iron(II) ions form an orange-colored complex compound with 1,10-phenanthroline. Iron(III) is reduced by a suitable reducing agent to iron(II) and is also detected. A buffer adjusts the pH. This orange-red phenanthroline complex is stable in the pH range of 2.5–9.
The described method detects dissolved iron and easily soluble iron compounds.
Following test kits are based on this method: VISOCOLOR Powder Pillows Iron, NANOCOLOR Iron, NANOCOLOR ECO Iron.
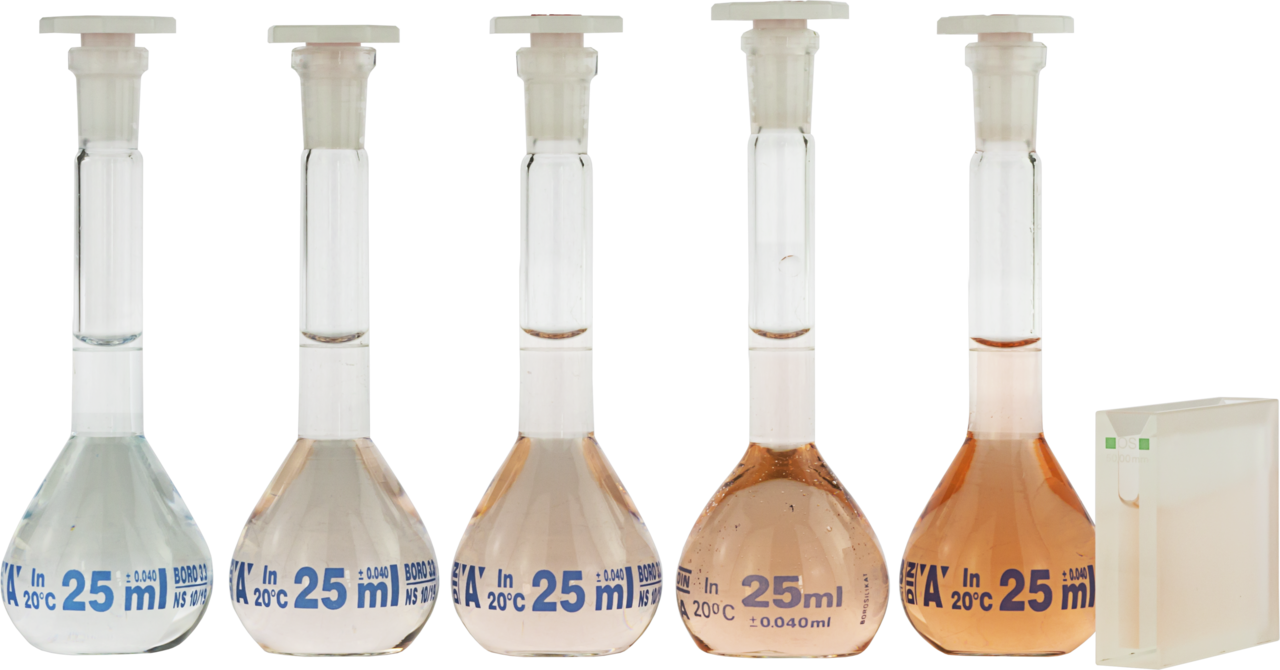


Distinction between total iron and dissolved iron
Dissolved iron comprises only the iron compounds present in the sample in completely dissolved form. Prior to analysis, filtration of the sample with the membrane filtration kit 0.45 µm is recommended.
For determination of total iron, decomposition with the reagent NANOCOLOR NanOx Metal or with the decomposition kit is required.
Differentiation of iron(III) and iron(II)
It is possible to distinguish between the two different oxidation states of iron in two tests:
VISOCOLOR ECO Iron 2 and the standard test NANOCOLOR Iron.
Sample preservation
- After adjusting the pH value to 1–2 with nitric acid, the sample can be preserved for storage for up to 1 month (storage vessel: PE or glass bottle).
- After adjusting the pH value to 1-2 with hydrochloric acid 2, iron(II) compounds can be stored for up to 7 days.
Fe2+ can be discriminated from Fe3+ by omissing the reducing agent.
Tips & tricks
Decomposition
-
For the simultaneous detection of iron complexes and determination of total iron, the sample must be oxidatively decomposed with NANOCOLOR NanOx Metal or the decomposition kit prior to analysis.
Background information
-
In the determination of iron in aqueous samples it must be noted that the previously mentioned processes will occur after sampling as well. Therefore, differentiated determination of forms present must be done directly on site. If this is not possible, the sample should be stabilized, if possible, by a few drops of acid (use depending on the parameters to be determined).
Filtration
-
To determine only “dissolved iron”, samples of turbid waters must be filtered prior to analysis.
Sea water suitability
- Almost all VISOCOLOR and NANOCOLOR Iron tests are suitable for sea water analysis. The exception is the test VISOCOLOR HE Iron which does not allow sea water analysis. For more information, please refer to the respective instruction leaflet.
pH
- The pH values which are stated in the instruction leaflets for the sample solution must be complied with. If necessary, adjust the pH with nitric acid or sodium hydroxide.
Interferences
- Oxidants interfere with the determination in the test NANOCOLOR Iron 3.
- Other metal ions such as cobalt or nickel disturb the test at various concentrations, depending on the test. The concentration from which on interference is to be expected is specified in the respective instruction leaflets.
- Further interfering ions are listed in the instruction leaflets.
Turbidity
Turbid samples have to be filtered; turbidity leads to incorrect results: For coarsely dispersed turbidities, use qualitative filter paper (e.g. MN 615), for moderately dispersed turbidities, use glass-fiber paper (e.g. MN 85/70 BF) or membrane filtration set GF/PET 0.45 µm, for finely dispersed turbidities, use membrane filtration kit 0.45 µm or GF/PET 0.45 µm.
 Standard solution NANOCONTROL Multistandard Drinking water
Standard solution NANOCONTROL Multistandard Drinking water